Psoriasis may be found on any part of the skin but is usually found on the scalp, knees, elbows and lower back.
Psoriasis is not an infection. You can't catch it by touching the affected skin of someone who's got it.
What Causes Psoriasis?
Immune System
 |
| Immune system |
The immune system plays a key role in psoriasis.
If you have psoriasis, your white blood cells known as T cells attack healthy skin cells by mistake, as if it were fighting an infection.
This mistaken attack causes new skin cells to develop too quickly, resulting ultimately in elevated scaling plaque of psoriasis.
If you have psoriasis, your white blood cells known as T cells attack healthy skin cells by mistake, as if it were fighting an infection.
This mistaken attack causes new skin cells to develop too quickly, resulting ultimately in elevated scaling plaque of psoriasis.
Genetics
 |
| Genetics |
Psoriasis has a strong hereditary component, and many genes are associated with it.
If you have a family member with the condition, your risk for developing psoriasis is higher.
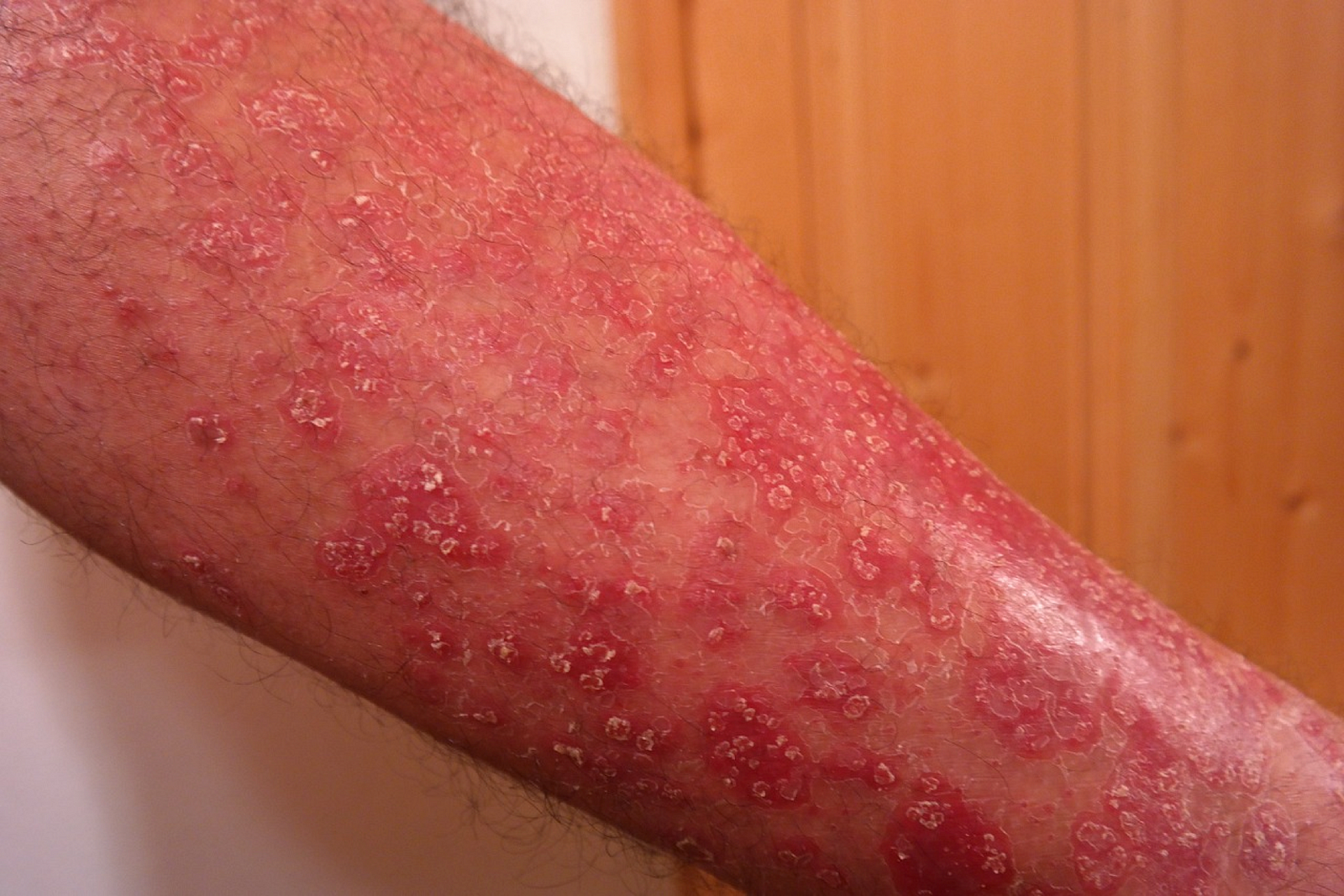
Psoriasis symptoms vary from person to person and depend on the type of psoriasis. They can range from from small patches to complete body coverage. Psoriasis typically presents as red, flaky, crusty patches with white scales on top. The patches can be itchy, uncomfortable, and they may bleed easily if you rub or pick them.
There are five main types of psoriasis.
If you have a family member with the condition, your risk for developing psoriasis is higher.
What are the symptoms?
What are the different types of psoriasis?
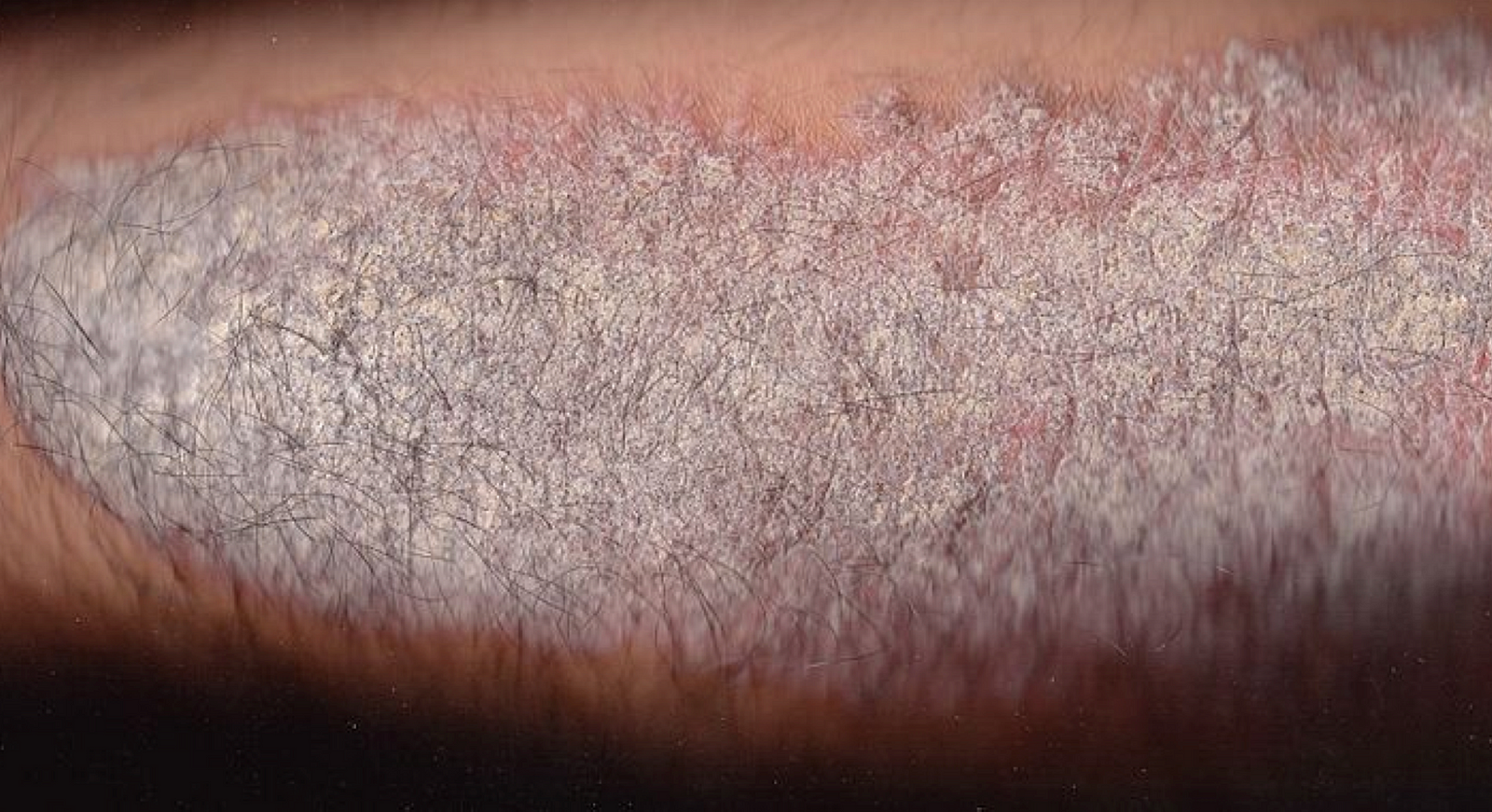
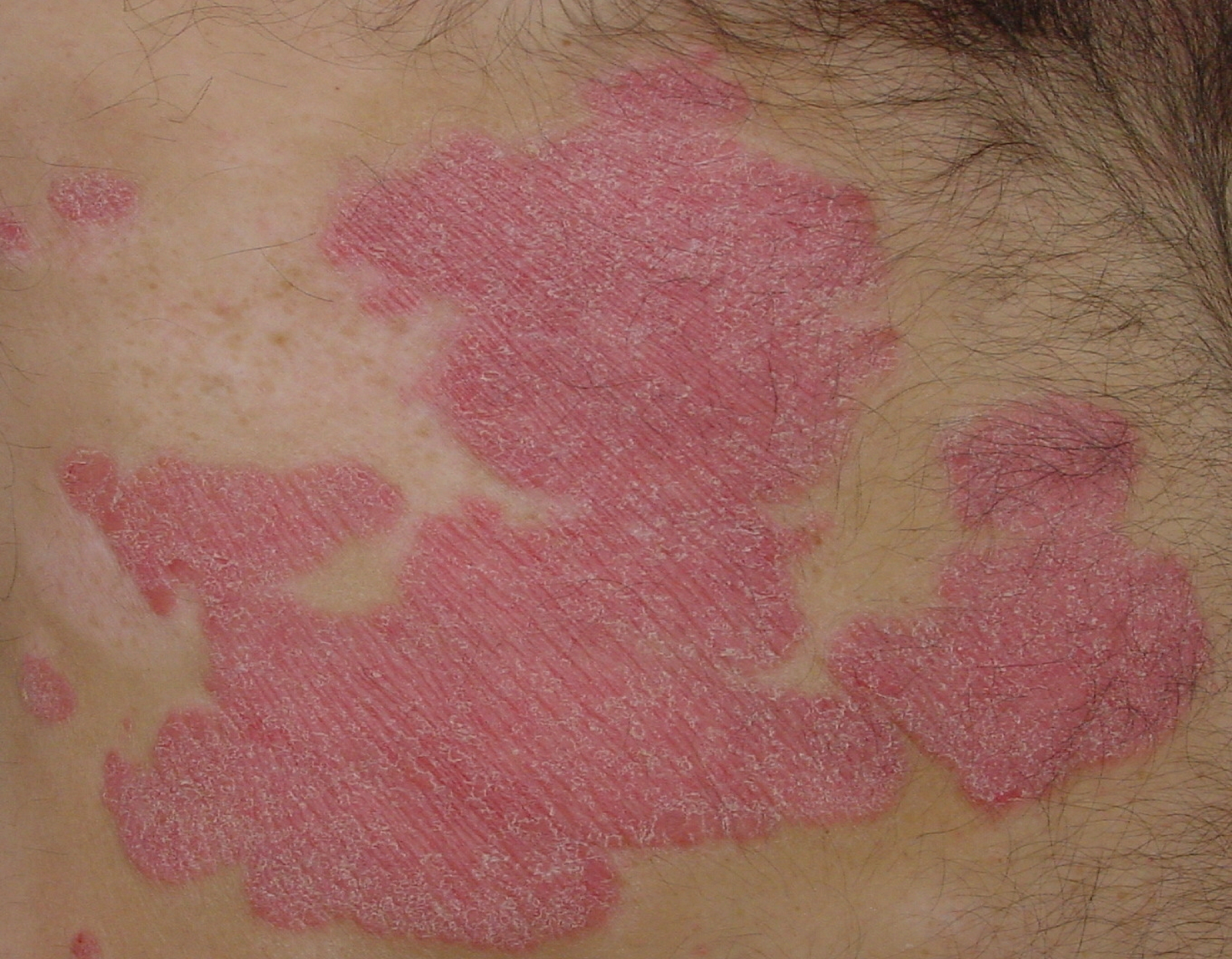
1. Plaque Psoriasis
 |
| Plaque psoriasis |
Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form of psoriasis. It causes dry, raised, red patches with white scales on top.
The plaques might be itchy and can occur anywhere on the body, including shins, navel area, scalp, the back of the forearms, genitals and the soft tissue inside the mouth.
The plaques might be itchy and can occur anywhere on the body, including shins, navel area, scalp, the back of the forearms, genitals and the soft tissue inside the mouth.
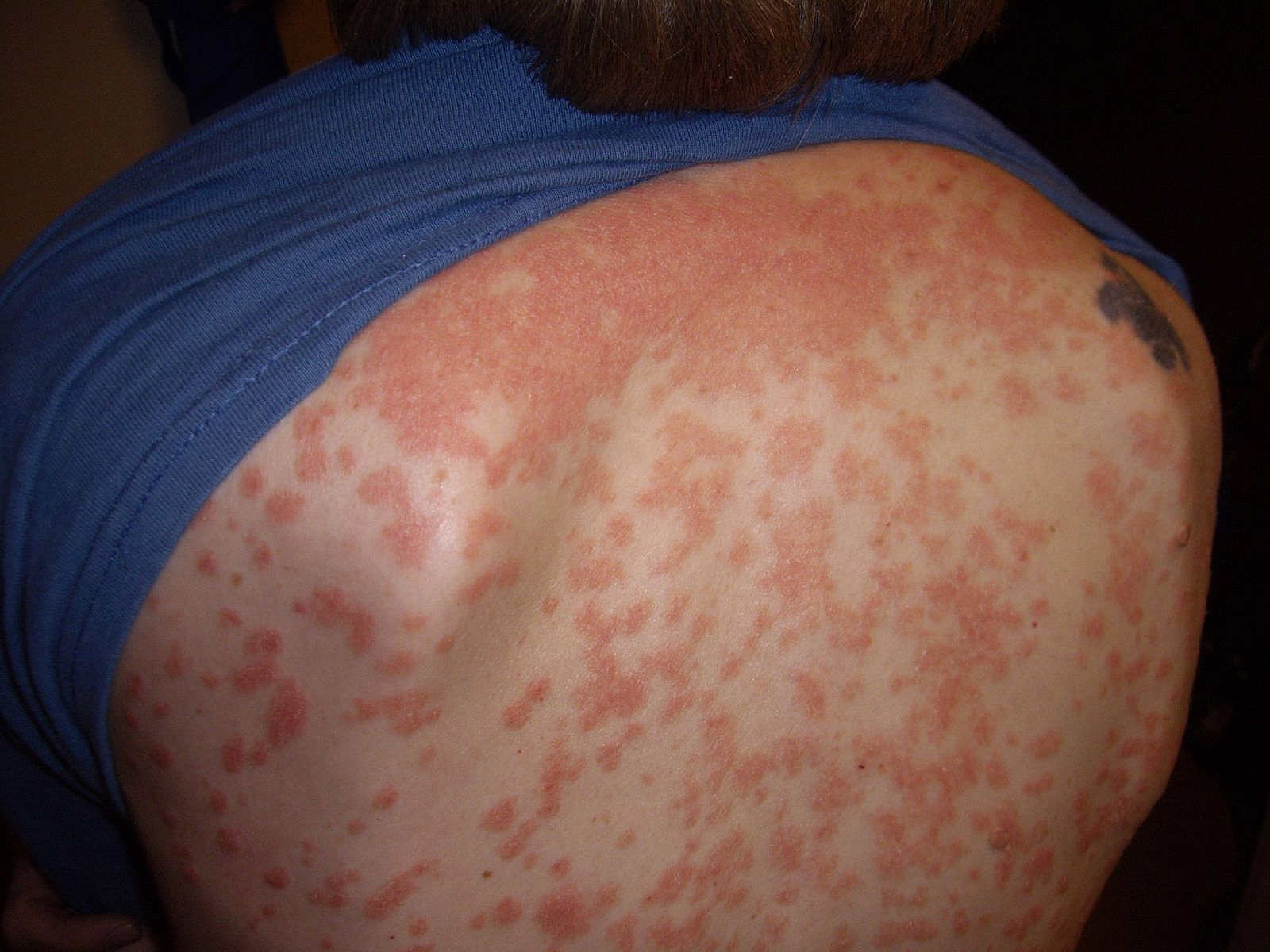
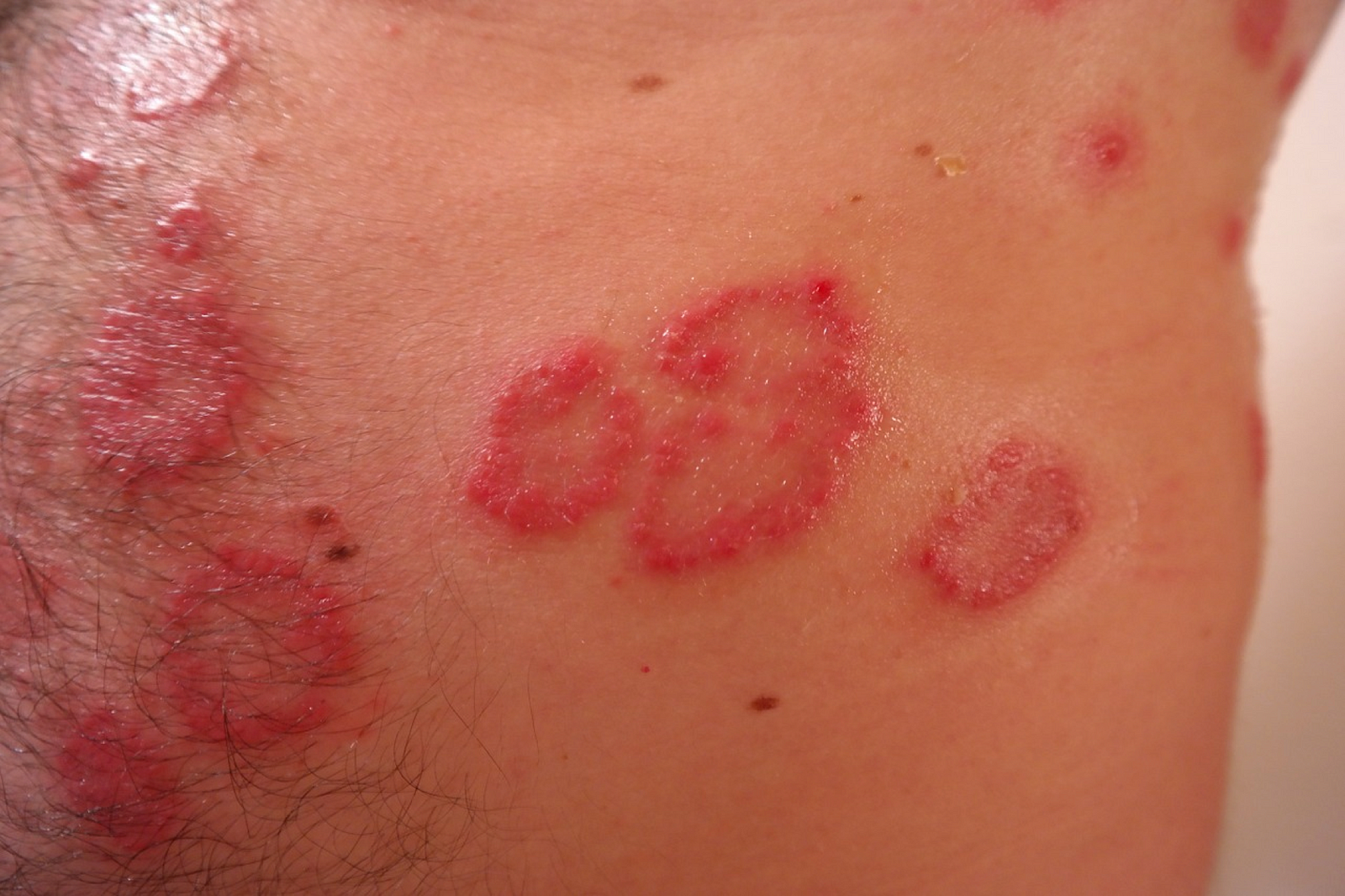
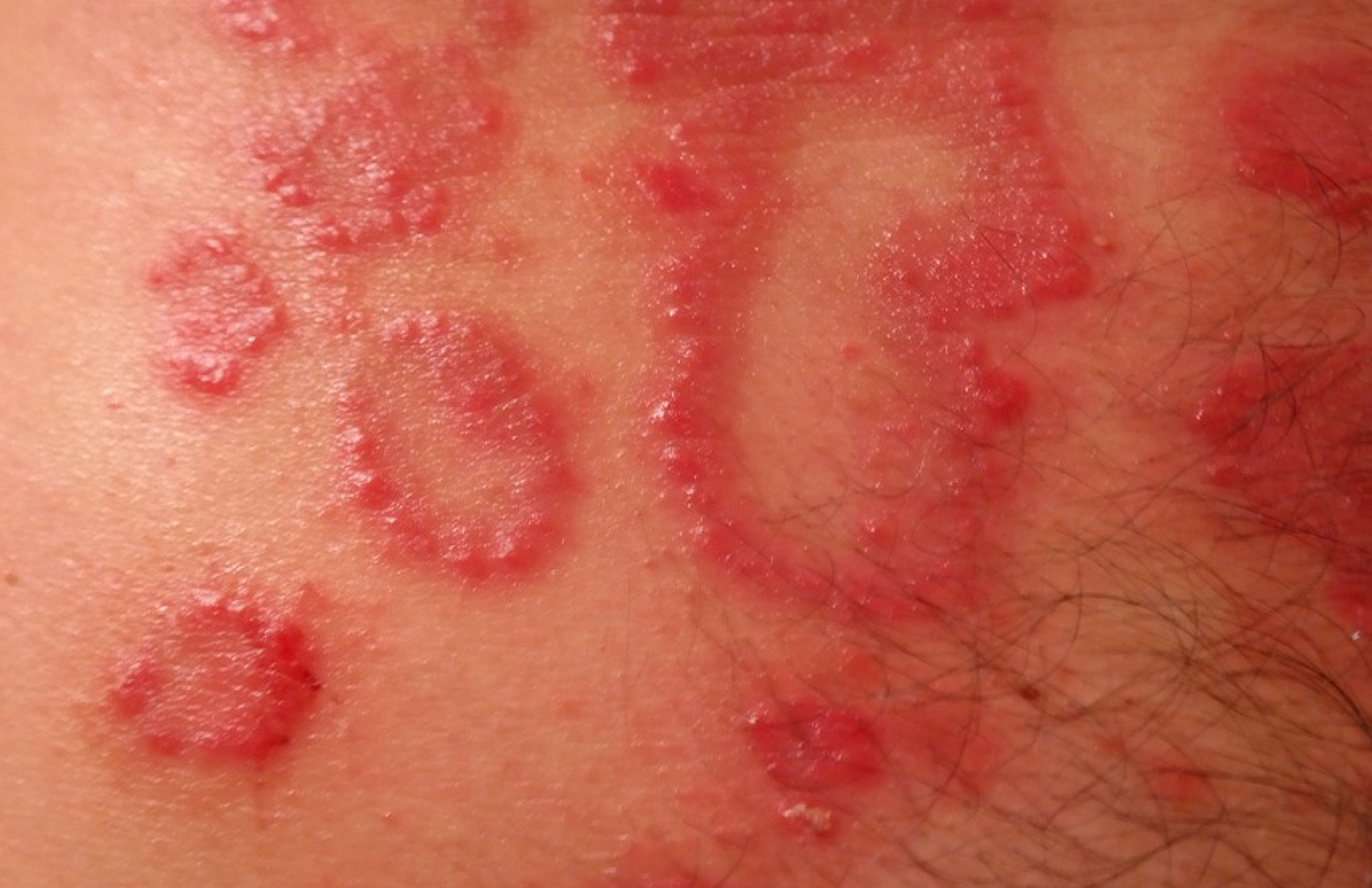
2. Guttate Psoriasis
 |
| Guttate psoriasis |
Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. This type primarily affects young adults and children. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the torso, arms, legs and scalp.
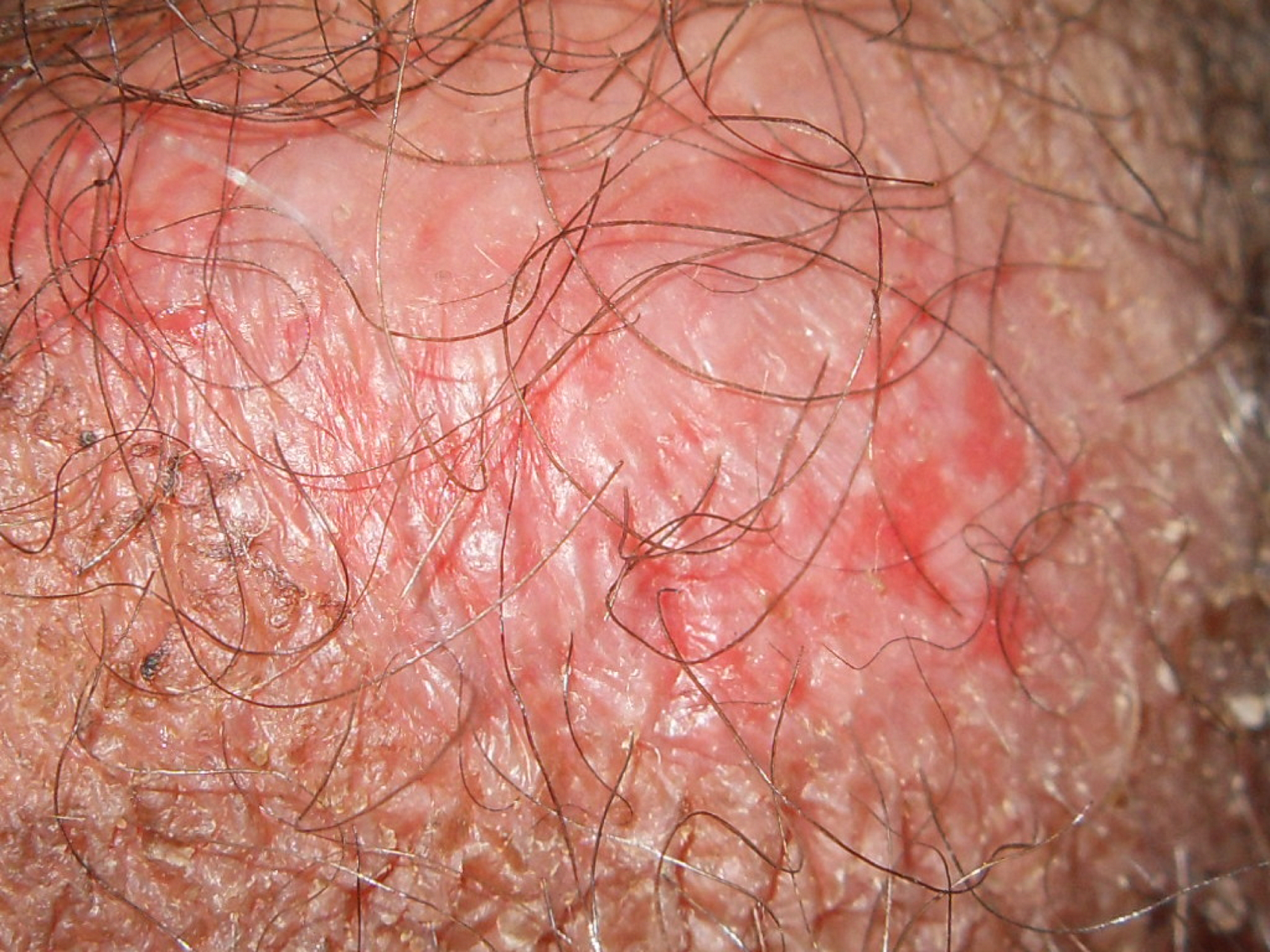
3. Inverse Psoriasis
 |
| Inverse psoriasis |
Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. The patches develop under the breasts, in the armpits, in the groin and around the genitals.
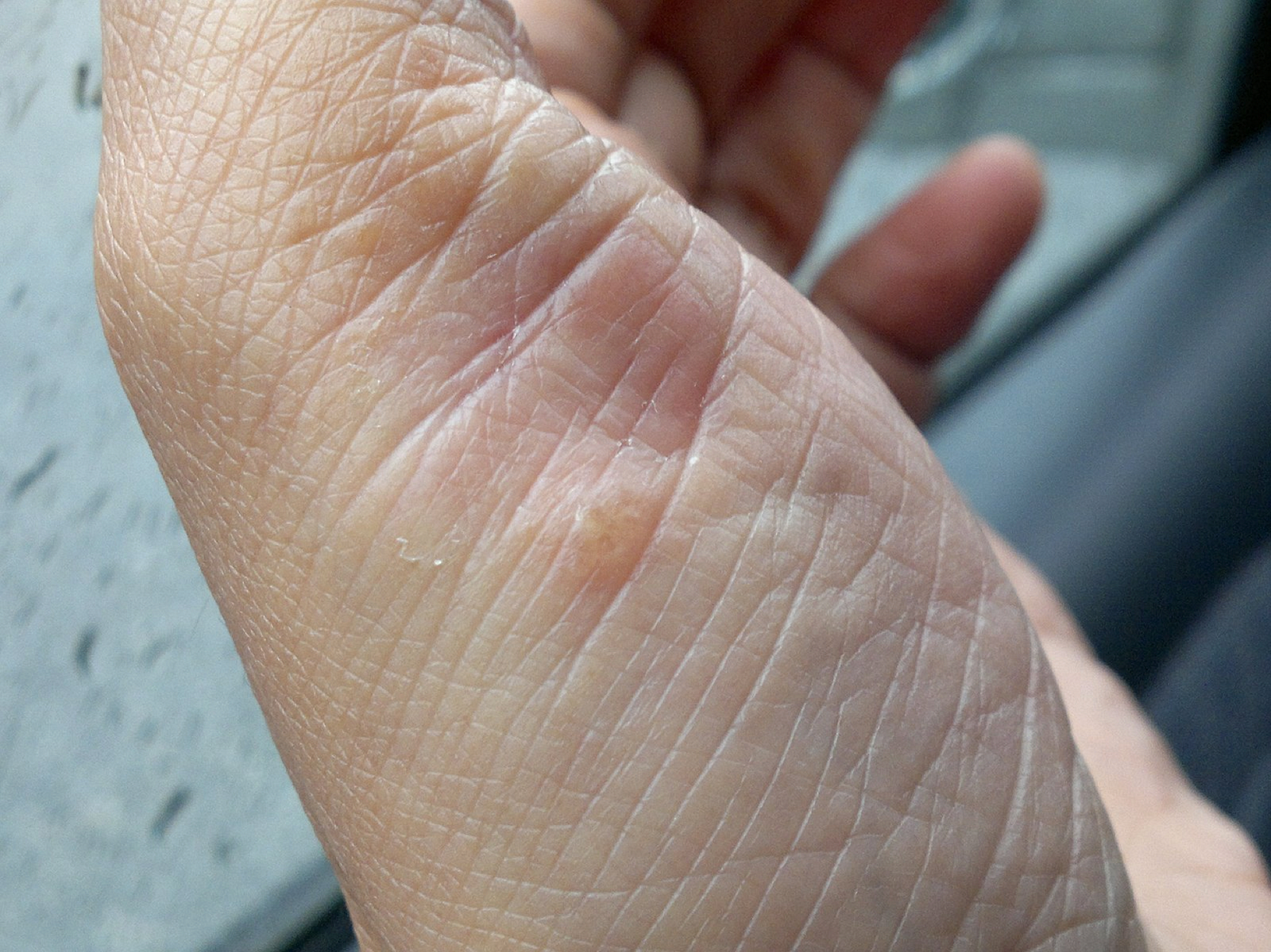
4. Pustular Psoriasis
 |
| Pustular psoriasis |
Pustular psoriasis presents as small non-infectious pus-filled blisters. The blisters may come and go frequently.
Pustular psoriasis can occur in widespread patches or in smaller areas on your hands, feet or fingertips.
Pustular psoriasis can occur in widespread patches or in smaller areas on your hands, feet or fingertips.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
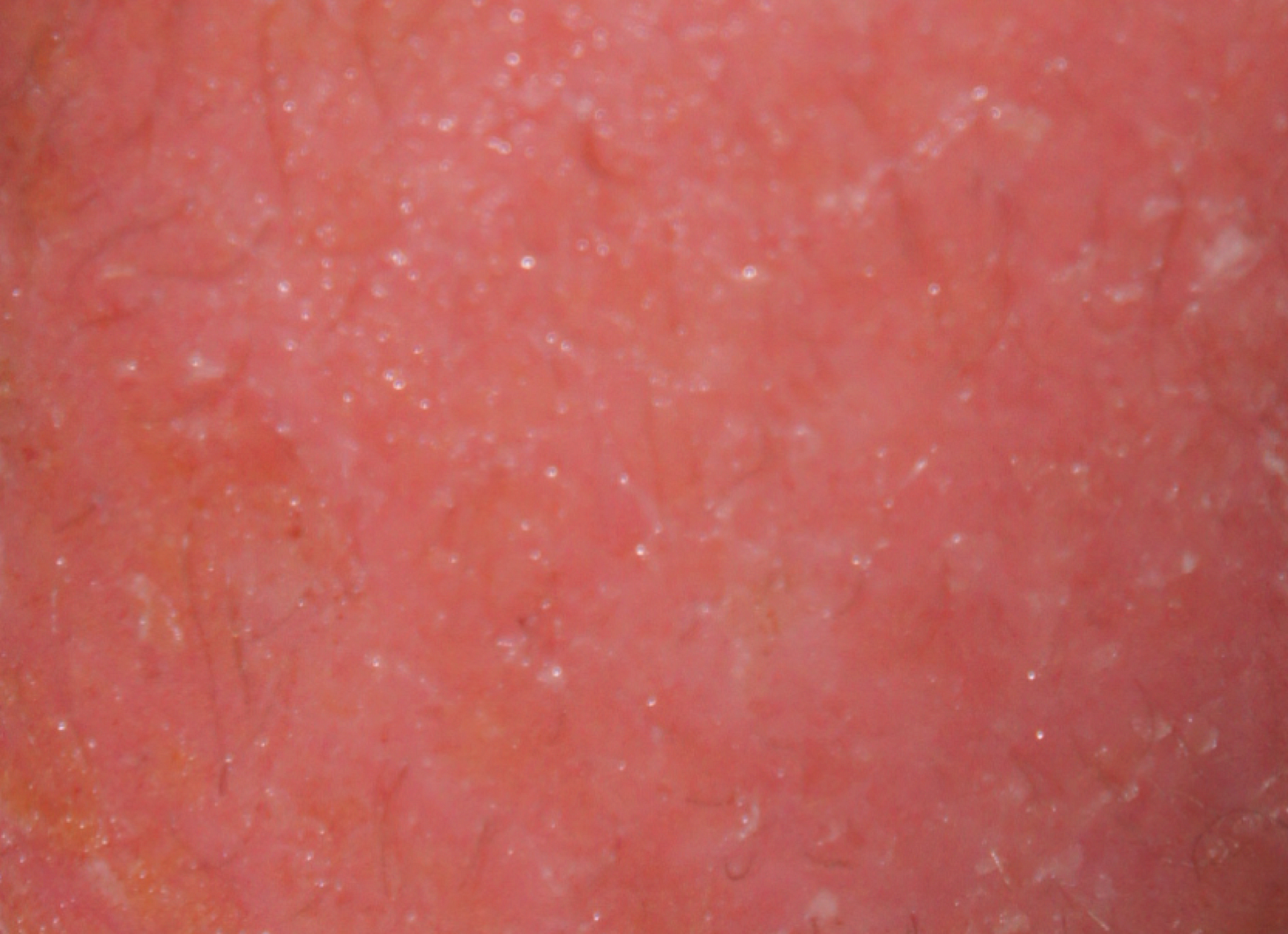 |
| Erythrodermic psoriasis |
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a very rare and severe type of psoriasis. It occurs when the rash becomes very widespread. The rash can cover your entire body that can itch or burn intensely.
There is no cure for psoriasis. However, various treatments can help control the symptoms.
If you suspect that you may have psoriasis, see your doctor for an examination.
Final Thoughts
If you suspect that you may have psoriasis, see your doctor for an examination.
#psoriasis #psoriasistreatment #psoriasiscauses #psoriasissymptoms #skin #skindiseases #immunesystem #rash #skinrashes #plaquepsoriasis #scalppsoriasis #psoriasiscure #scalyskin #rashes #health
Comments
Post a Comment